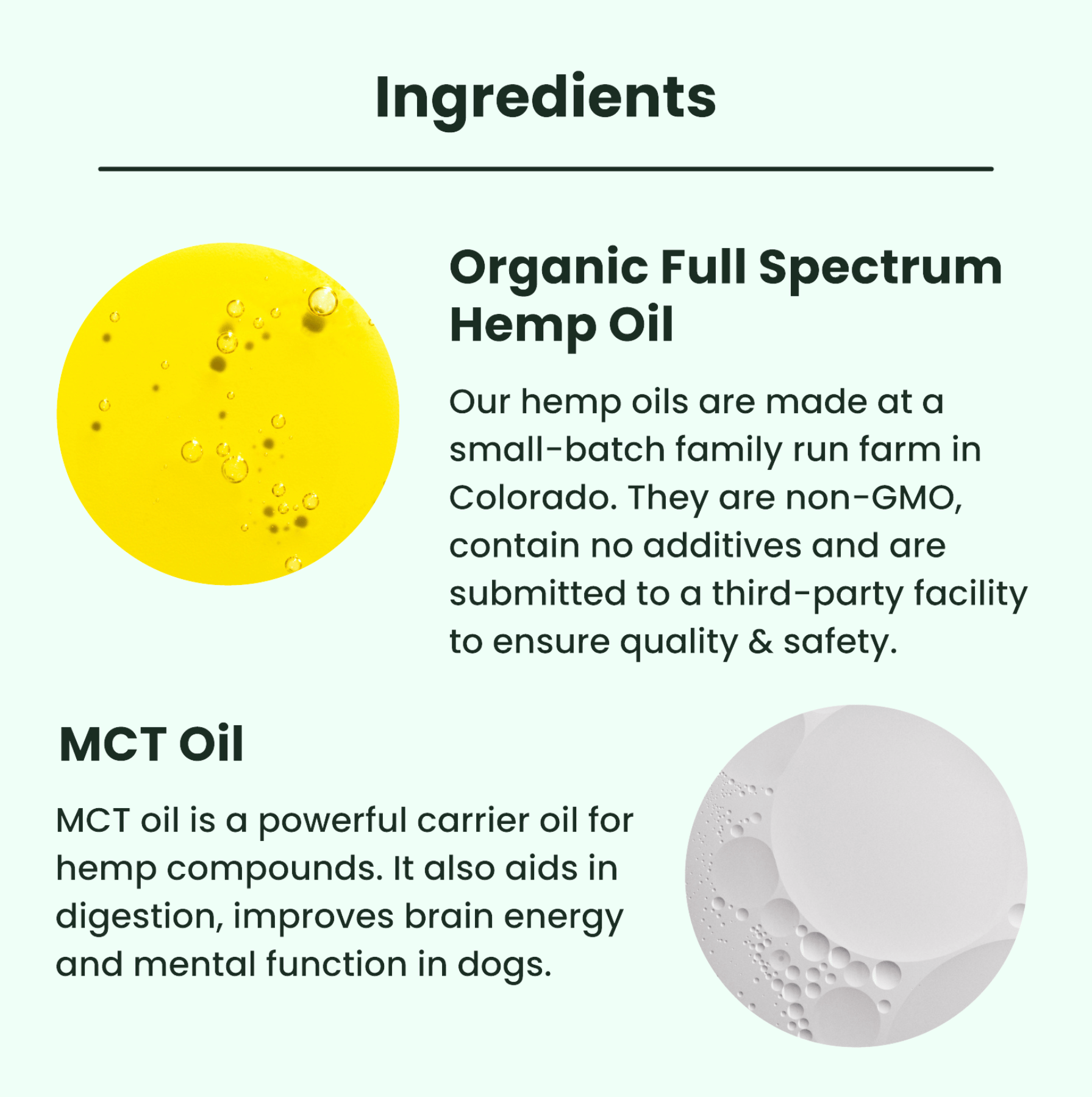
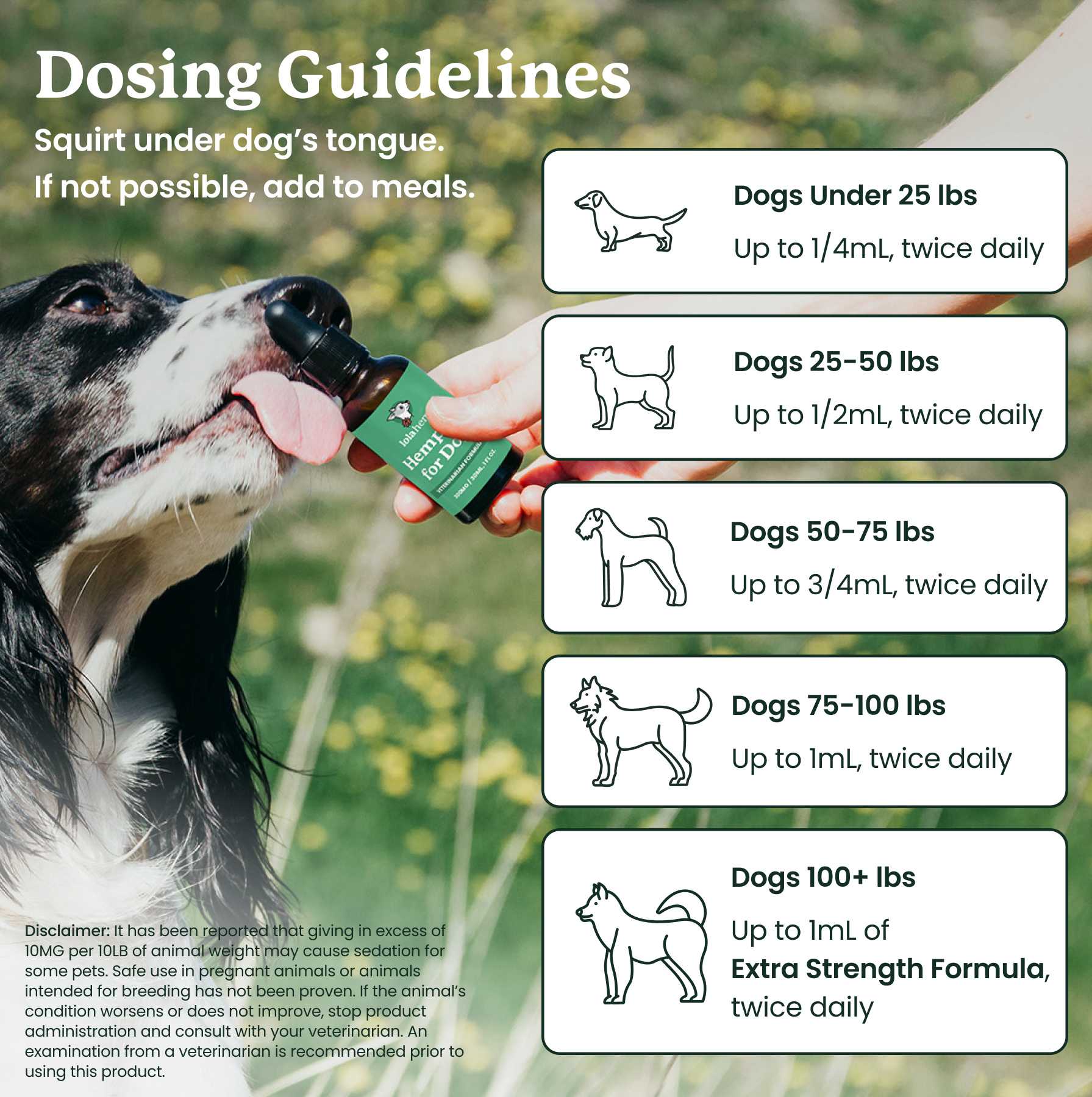
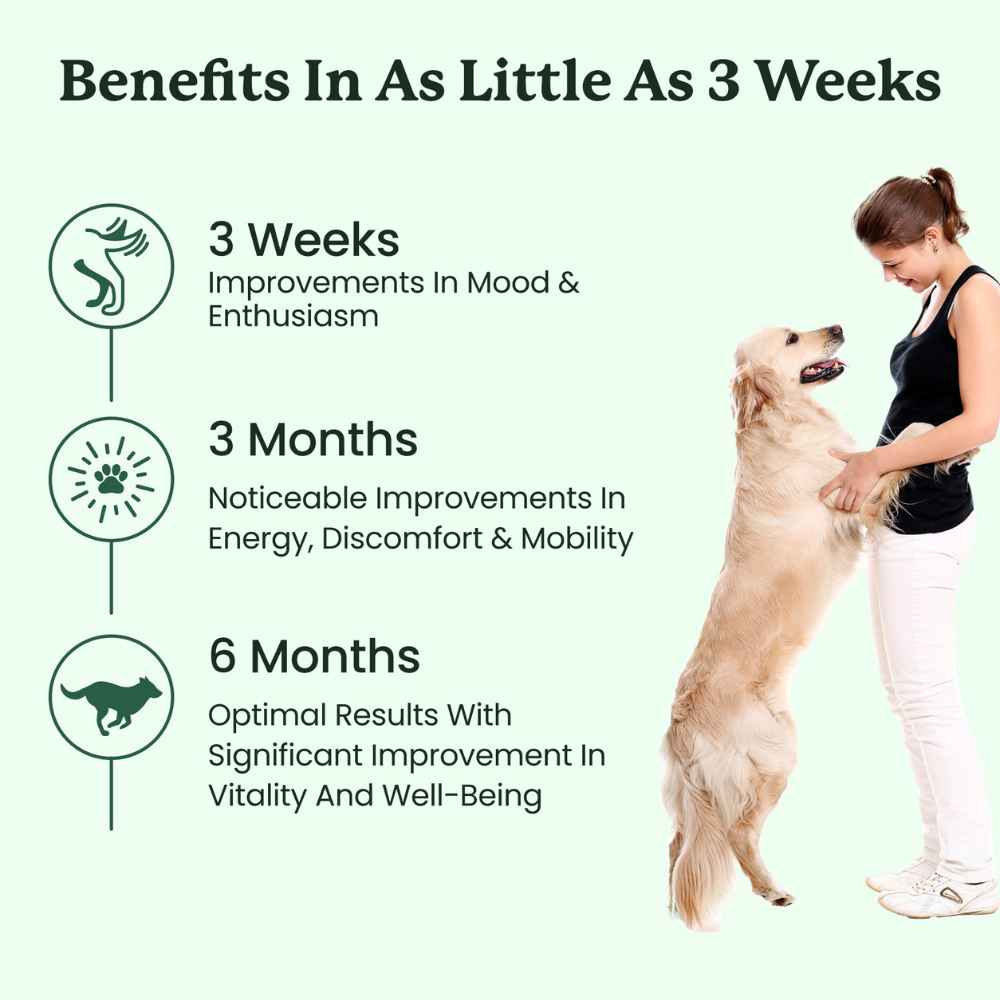
When it comes to CBD, many resources discuss its effects on the endocannabinoid system. But what is this mysterious body system? How does it work, and how does CBD work with it? Read on for a crash course on the endocannabinoid system, its parts, its role in your body, and more.
What Is the Endocannabinoid System in Dogs?
The endocannabinoid system (ECS) is a natural biological system found in all mammals — including dogs, cats, and humans. This complex system plays a vital role in maintaining balance within the body and supporting overall wellness.
The ECS is made up of tiny components—endocannabinoids, receptors, and enzymes—that are too small to see, yet essential for life. It functions independently of cannabis or CBD use, meaning your dog’s ECS is active whether or not they’ve ever been exposed to cannabinoids.
The ECS was named after cannabinoids like CBD and THC because these compounds were discovered before scientists understood how they interacted with this system.
The Endocannabinoid System and Canine Homeostasis
The primary job of the ECS is to maintain balance — known as homeostasis. This means keeping vital systems like temperature, mood, sleep, and appetite within a healthy range.
For example, the ECS helps regulate body temperature by sending signals to various organs when your dog is too hot or too cold. Similar processes occur in digestion, pain response, and immune regulation. In short, the ECS keeps your dog’s body in balance.
Parts of Your Dog's Endocannabinoid System
The ECS has three main parts:
- Endocannabinoids: Naturally produced molecules (like anandamide and 2-AG) that carry messages between cells to promote balance.
- Receptors (CB1 and CB2): These sit on cell surfaces and receive endocannabinoid messages. CB1 receptors are found mostly in the brain and nerves, while CB2 receptors are found in immune cells and tissues.
- Enzymes (FAAH and MAGL): These break down endocannabinoids after use, preventing overstimulation and maintaining equilibrium.
What's the Purpose of the Canine Endocannabinoid System?
The ECS interacts with nearly every organ and biological process, making it one of the body’s most influential regulatory systems. Research is ongoing, but scientists know the ECS helps regulate inflammation, pain response, appetite, mood, and more.
The ECS and Joint Health in Dogs
One of the ECS’s most studied roles in dogs is joint health. Many pet owners report improved mobility and comfort after using cannabinoid-based supplements designed to support joint function and reduce inflammation.
1. Memory
The CB1 receptor is linked to memory regulation and the healthy “forgetting” of old information to make room for new learning. Research also suggests CBD may help support new brain cell growth in the hippocampus, which aids memory retention.
2. Appetite
The ECS helps regulate appetite through interactions between CB1 receptors and the brain’s hypothalamus. THC strongly activates this system, causing the well-known “munchies,” while CBD supports more subtle appetite balance in dogs.
3. Sleep
The ECS supports healthy sleep cycles by influencing levels of the endocannabinoid anandamide. Anandamide works with the brain chemical adenosine to promote relaxation and restful sleep — the opposite of caffeine’s stimulating effect.
4. Exercise
Endocannabinoids like anandamide are partly responsible for the “runner’s high.” These natural molecules increase during exercise, improving mood and reducing stress for both humans and dogs.
The Endocannabinoid System: Key Takeaways
The endocannabinoid system is a vital regulator of the body’s internal balance, known as homeostasis. It supports the brain, immune system, and joints — among many other processes.
CBD and other plant-based cannabinoids interact with the ECS in gentle, supportive ways. While THC binds directly to receptors, CBD supports the ECS indirectly in dogs, helping promote calm, mobility, and overall wellness.
Frequently Asked Questions about the Endocannabinoid System in Dogs
What does the endocannabinoid system do in dogs?
The ECS helps regulate balance (homeostasis) in your dog’s body — including appetite, mood, pain response, inflammation, and sleep cycles.
Do dogs naturally have cannabinoids in their body?
Yes. Dogs produce natural cannabinoids called endocannabinoids, which interact with ECS receptors to maintain health even without CBD or cannabis use.
How does CBD affect the endocannabinoid system?
CBD doesn’t bind directly to ECS receptors like THC does. Instead, it supports natural endocannabinoid activity and helps extend their beneficial effects in the body.
Can the ECS help with inflammation in dogs?
Yes. The ECS plays a key role in managing inflammation, and activating ECS pathways may help soothe discomfort and support joint mobility.
Do all mammals have an endocannabinoid system?
Yes. All mammals — including dogs, cats, and humans — have an ECS that helps regulate essential physiological functions and overall balance.